What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a popular trading strategy where traders aim to profit from short- to medium-term price movements in financial markets. Swing traders hold stocks or other assets for a few days to a few weeks, depending on how the price fluctuates.
The goal of swing trading is to “capture a swing” in the market—whether the price is moving up or down. Swing traders analyze market trends and use technical analysis to identify potential entry and exit points. This method requires patience, as traders need to wait for trends to develop before making decisions.
In the Indian market, swing trading is commonly used by traders to take advantage of market volatility, especially in sectors like technology, finance, and pharmaceuticals and top nifty50 stocks. Beginners interested in swing trading often find it easier to start than other forms of trading since it doesn’t require constant monitoring but still offers the potential for significant returns.
Key Points to Remember:
- Swing trading is ideal for those looking to earn profits on medium-term price movements.
- It involves holding positions for several days or weeks, not hours.
- Traders rely on technical analysis and market trends to make decisions for swing trading..
- In India, swing trading can be a good way for beginners to learn and gain trading experience without the high-stakes pressure of day trading.
How to select stocks for Swing trading for beginners?
Selecting the right stocks is crucial for successful swing trading. Since swing traders focus on short- to medium-term gains, they need stocks that are likely to show noticeable price movement within a short period. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help beginners in selecting stocks for swing trading, especially within the Indian market.
Step 1. Look for Liquid Stocks
- Why: Liquidity refers to how easily a stock can be bought or sold. Liquid stocks have a high trading volume, meaning there are plenty of buyers and sellers, which allows you to enter and exit positions easily.
- How to Do It: Focus on stocks listed in major indices like Nifty 50 or BSE Sensex, as they tend to have high liquidity. Check the average daily trading volume, and avoid stocks with low trading activity.
- Tip: Use volume indicator for daily trading volume visualization on chart.
Step 2. Select Volatile Stocks
- Why: Volatile stocks experience significant price movements, which is necessary for capturing profitable moves in swing trading. Low-volatility stocks often don’t provide enough movement to make swing trades worthwhile.
- How to Do It: Use volatility indicators, such as Average True Range (ATR), to identify stocks with the potential for large price swings. Stocks from sectors like technology and banking in the Indian market often display good volatility.
3. Analyze Stock Trends
- Why: Swing traders aim to trade with the trend, whether upward or downward. Understanding the current trend can help you make more informed decisions.
- How to Do It: Use trendlines or moving averages to identify whether a stock is in an uptrend or downtrend. If a stock is consistently making higher highs and higher lows, it’s in an uptrend and could be a potential buy. Conversely, if it’s making lower highs and lower lows, it might be suitable for a short position.
4. Use Technical Indicators for Confirmation
- Why: Technical indicators help confirm your trading signals and ensure you are making data-driven decisions. They can highlight potential entry and exit points.
- How to Do It: Beginners can use simple indicators like:
- Moving Averages: To identify overall trends. A 50-day moving average, for example, can show you if a stock is trending up or down.
- RSI (Relative Strength Index): To spot overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 indicates overbought conditions, while below 30 suggests oversold, signaling potential reversals.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): To determine the strength and direction of a trend.
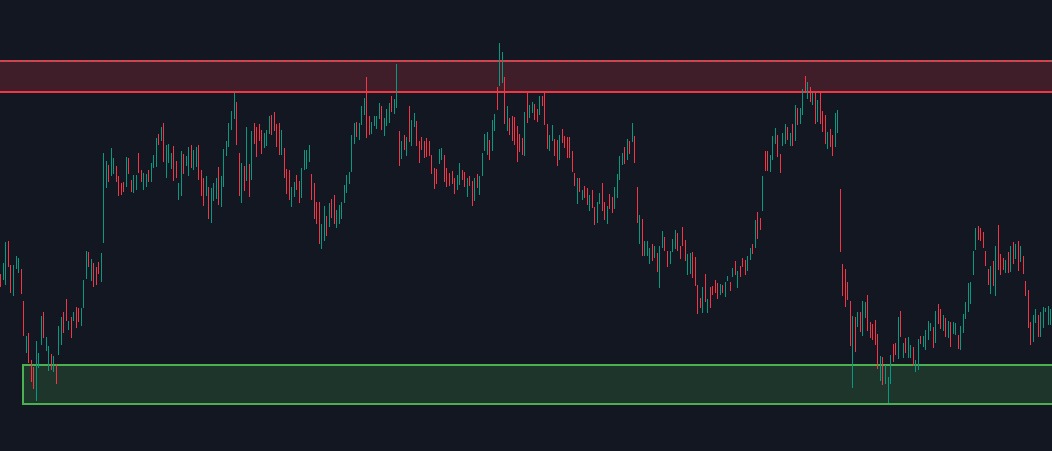
5. Identify Key Support and Resistance Levels
- Why: Support and resistance levels can help you decide where to enter or exit a trade. Buying near support levels and selling near resistance levels is a common swing trading tactic.
- How to Do It: Use historical price charts to find areas where the stock has repeatedly found support (a price it tends to stop falling) or resistance (a price it tends to stop rising).
In the below image, the red colored level is resistance level from where the price falls down. And the green colored level is the support level from where the price again starts to go upside.
6. Consider News and Earnings Reports
- Why: News, earnings announcements, and economic reports can significantly impact stock prices. Being aware of these can help you anticipate price swings.
- How to Do It: Track the news for the stocks you’re interested in. Earnings season, for example, often creates volatility, which can be beneficial for swing traders. Websites like Moneycontrol and Economic Times provide reliable updates for the Indian market.
- Tip: Use moneycontrol app to get an eye on all market related news.
7. Check the Stock’s Sector Performance
- Why: A strong-performing sector can provide tailwinds for individual stocks. If a sector is trending positively, its stocks may also be more likely to trend upward.
- How to Do It: Look at the performance of sectors on indices like Nifty 50 or BSE Sensex. If the IT sector is doing well, for example, consider swing trading top-performing tech stocks.
Quick Tips for Beginners
- Use a Stock Screener: Platforms like Zerodha’s Kite or Angel One’s app have built-in screeners to filter stocks based on criteria like volume, trend, or RSI levels. Here are some stock screeners.
- Start with a Few Stocks: Don’t overwhelm yourself by tracking too many stocks. Pick 5-10 stocks and get familiar with their trading behavior.
- Paper Trade First: Practice your strategy in a demo account before committing real money to understand how the stocks you select perform over time.
Difference between swing trading and intraday trading
Swing trading and intraday trading are both different trading strategies. Both have its own benefits and consequences. Like if you want to do it as a side business and don’t want to look at screen whole day, then swing trading is best for you. Meanwhile intraday trading is for those who are passionate in chart reading and technical analysis.
| Aspect | Swing Trading | Intraday Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Holding Period | A few days to a few weeks | Within the same trading day; no overnight positions |
| Time Commitment | Moderate; periodic monitoring throughout the day | High; requires constant monitoring during market hours |
| Number of Trades | Fewer trades; typically 5-10 per month | Many trades; often multiple trades in a single day |
| Risk Level | Moderate risk; exposed to overnight and weekend gaps | Higher risk; price fluctuations can be rapid and unpredictable |
| Profit Potential | Targets larger price swings; potential for higher returns over days/weeks | Smaller gains per trade; relies on frequent trades to accumulate profits |
| Stress Level | Generally lower; more relaxed pace and more time to make decisions | High; fast-paced and requires quick decision-making |
| Technical Analysis | Uses both technical and fundamental analysis | Primarily relies on technical analysis and quick indicators |
| Transaction Costs | Lower; fewer trades mean lower brokerage and tax expenses | Higher; frequent trades increase transaction costs |
| Market Monitoring | Requires monitoring market trends but not constantly | Needs full attention during trading hours |
| Suited For | Part-time traders, beginners, or those with other commitments | Full-time traders, experienced traders, or those with high risk tolerance |
Pros and cons of swing trading
Swing trading can be an effective trading strategy for beginners and experienced traders alike. However, like any strategy, it has its advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a clear look at the pros and cons of swing trading, especially from the perspective of beginners.
Pros of Swing Trading
- Less Time-Intensive
- Unlike day trading, swing trading does not require constant market monitoring. This makes it suitable for people who have other businesses/jobs or cannot give full-time hours to trading.
- Potential for Significant Gains
- Swing trading targets larger price moves than day trading. By holding stocks over days or weeks, traders can capture more substantial price swings and potentially higher returns.
- Reduced Transaction Costs
- Fewer trades mean lower transaction fees and taxes compared to day trading, where frequent buying and selling can add up. Lower costs help preserve more of your profits over time.
- Less Stressful than Day Trading
- Swing trading involves a slower pace and more time to analyze trades, reducing the intensity and pressure often associated with day trading. This makes it more beginner-friendly and manageable.
- Combines Technical and Fundamental Analysis
- Swing trading allows you to leverage both technical indicators and fundamental factors. This approach provides more opportunities to learn and gain a deeper understanding of the stock market.
Cons of Swing Trading
- Risk of Overnight and Weekend Gaps
- Swing traders hold positions overnight and over weekends, which exposes them to unexpected market events and gaps. Bad news can lead to price drops, resulting in potential losses.
- Requires Discipline and Patience
- Swing trading demands patience, as traders need to wait for trends to develop. Impulsive decisions can lead to losses, so discipline is essential, which may be challenging for beginners.
- Moderate Time Commitment
- While not as time-intensive as day trading, swing trading still requires regular monitoring of open positions and analyzing charts and indicators. This time commitment might be challenging for people with busy schedules.
- Market Volatility Can Be Unpredictable
- Swing trading relies on short- to medium-term trends, but markets can be volatile and unpredictable. Beginners may find it challenging to handle sudden price changes that don’t follow expected patterns.
- Not Ideal for Small-Cap Stocks
- Small-cap stocks can be too volatile for swing trading. Large- and mid-cap stocks are generally more stable, but they may not always produce the big swings beginners expect, limiting some opportunities.
- Learning Curve for Technical Analysis
- Swing trading relies heavily on technical analysis tools like moving averages, RSI, and MACD. Beginners might find it challenging to learn and apply these tools effectively at first.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is Swing Trading Good for Beginners?
Yes, swing trading is often considered beginner-friendly because it doesn’t require constant monitoring like day trading. Beginners can learn about market trends and technical analysis at a manageable pace. Since swing trading involves holding positions for several days or weeks, it provides enough time to plan trades and learn from the results without the high pressure of intraday trading.
2. What is the 1% Rule in Swing Trading?
The 1% rule in swing trading is a risk management guideline that suggests you should never risk more than 1% of your trading capital on a single trade. For example, if you have ₹1,00,000 in your account, you would risk only ₹1,000 on a trade. This rule helps protect your account from large losses and allows you to stay in the game longer, especially as you’re learning and refining your strategies.
3. How Do I Start Swing Trading?
Step 1: Learn the Basics – Understand swing trading concepts, strategies, and technical indicators.
Step 2: Choose a Broker – Select a reliable broker with good trading tools, low fees, and a user-friendly interface.
Step 3: Develop a Strategy – Pick a swing trading strategy that suits your goals, like moving average crossovers or RSI-based reversal.
Step 4: Use a Demo Account – Most brokers offer demo accounts where you can practice your strategy without risking real money.
Step 5: Start Small – Begin with small trades, sticking to the 1% rule, and gradually increase as you gain experience and confidence.
Step 6: Stay Updated – Regularly check economic news and trends, especially in the Indian market, as these can impact stock prices.
4. Is Swing Trading Profitable?
Yes, swing trading can be profitable when done correctly, as it targets medium-term price swings that can yield good returns. However, profitability depends on factors like market knowledge, risk management, discipline, and strategy. Swing trading generally has a moderate risk-to-reward ratio, so consistent gains require a structured approach and practice. Beginners should be prepared to invest time in learning and may see smaller profits initially as they develop their skills.
5. Which Broker Should I Choose?
In India, popular brokers for swing trading include Zerodha, Angel One, Upstox, and ICICI Direct. Here’s what to look for:
Low Fees: Brokers with lower transaction costs are ideal for swing trading.
Good Trading Platform: Look for brokers with easy-to-use platforms that support technical analysis tools.
Availability of Research: Some brokers offer research reports and technical insights, which can be beneficial for beginners.
Demo Accounts: If you’re just starting, a broker that offers a demo account can help you practice without real financial risk.