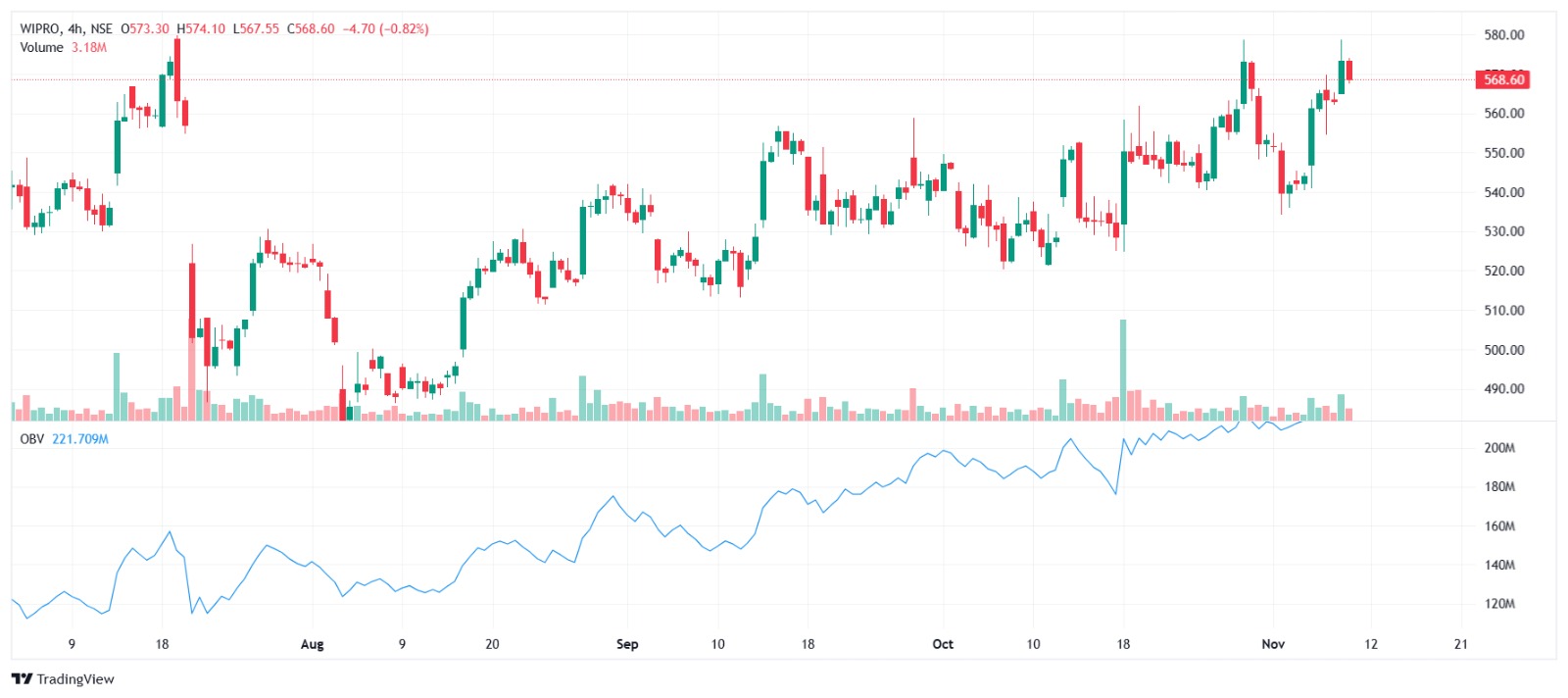
Swing trading is a popular trading style that captures price swings over a few days to several weeks. To successfully identify and act on these swings, traders use technical indicators to predict price movements and make informed decisions. This guide will walk you through the best indicators for swing trading and how to use them, even if you’re a complete beginner!
Why Use Technical Indicators for Swing Trading?
Technical indicators are tools based on price, volume, and other technical data that help traders to analyze trends and make trading decisions. For swing trading, they’re essential because they highlight patterns, reveal trends, and provide signals for entry and exit points. By learning these indicators, you can start making more informed decisions with your trades and become better at capturing winning trades.
Here Are The 10 Best Indicators For Swing Trading:
1. Moving Averages (MA)
Moving Averages are one of the most commonly used technical indicators for swing trading. They smooth out price data over a set period, providing a clearer view of the trend by reducing the noise of daily price fluctuations.
Types of Moving Averages:
- Simple Moving Average (SMA): Calculates the average price over a set period (e.g., 10, 50, or 200 days).
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA): Gives more weight to recent prices, making it quicker to respond to price changes.
How to Use Moving Averages in Swing Trading
- Trend Identification: A rising MA indicates an uptrend, while a falling MA suggests a downtrend.
- Crossover Strategy: When a shorter MA (like the 20-day EMA) crosses above a longer one (like the 50-day EMA), it signals a potential uptrend. Conversely, when the shorter MA crosses below, it may indicate a downtrend.
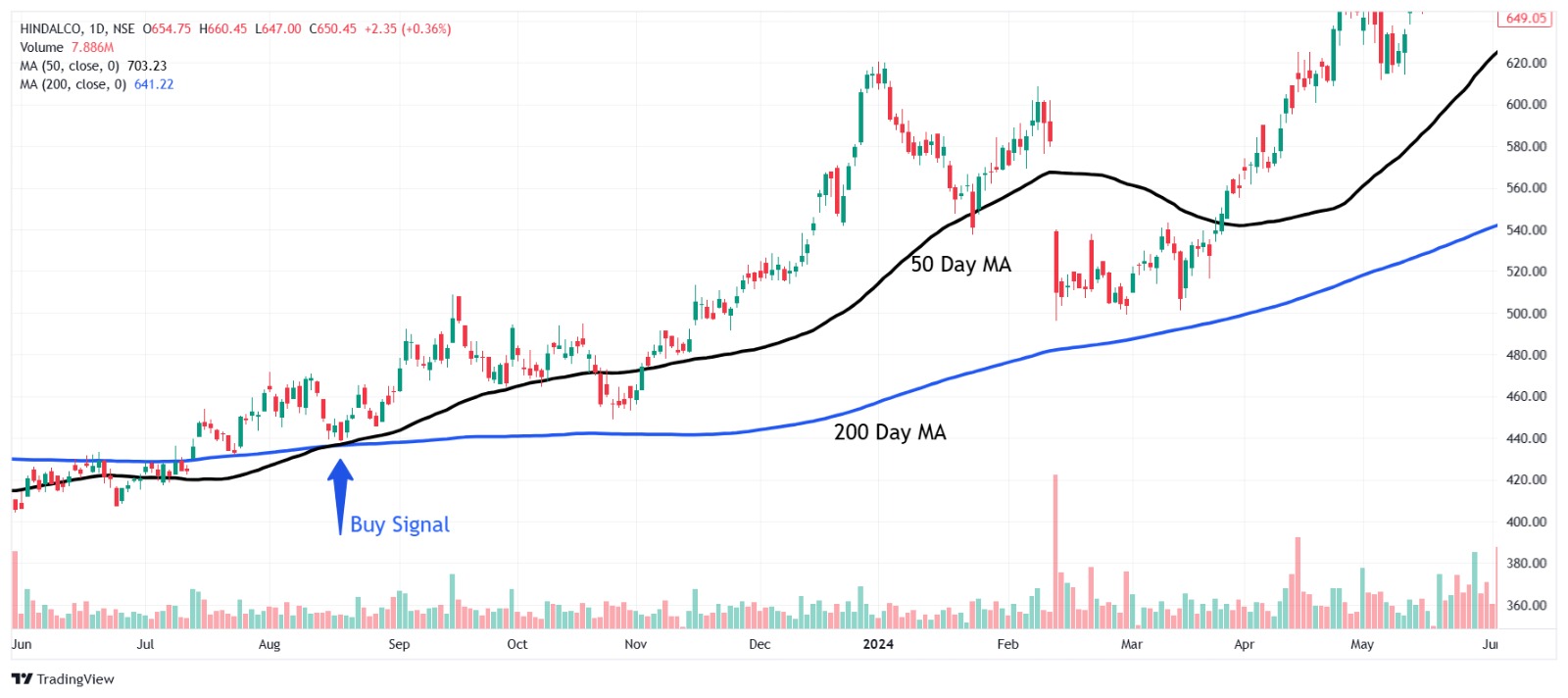
This is a One-Day Chart of Hindalco, where the 50-day MA has crossed over the 200-day MA and given an upside indication.
2. Relative Strength Index (RSI)
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. RSI values range from 0 to 100, and it’s typically used to identify overbought or oversold conditions.
How to Use RSI for Swing Trading
- Overbought and Oversold Levels: When RSI is above 70, it indicates the stock or asset might be overbought and could be due for a pullback. When RSI is below 30, the asset or stock might be oversold, signalling a potential upward movement.
- Divergence: If the price is making new highs but the RSI is not, it could be a sign of an impending reversal.
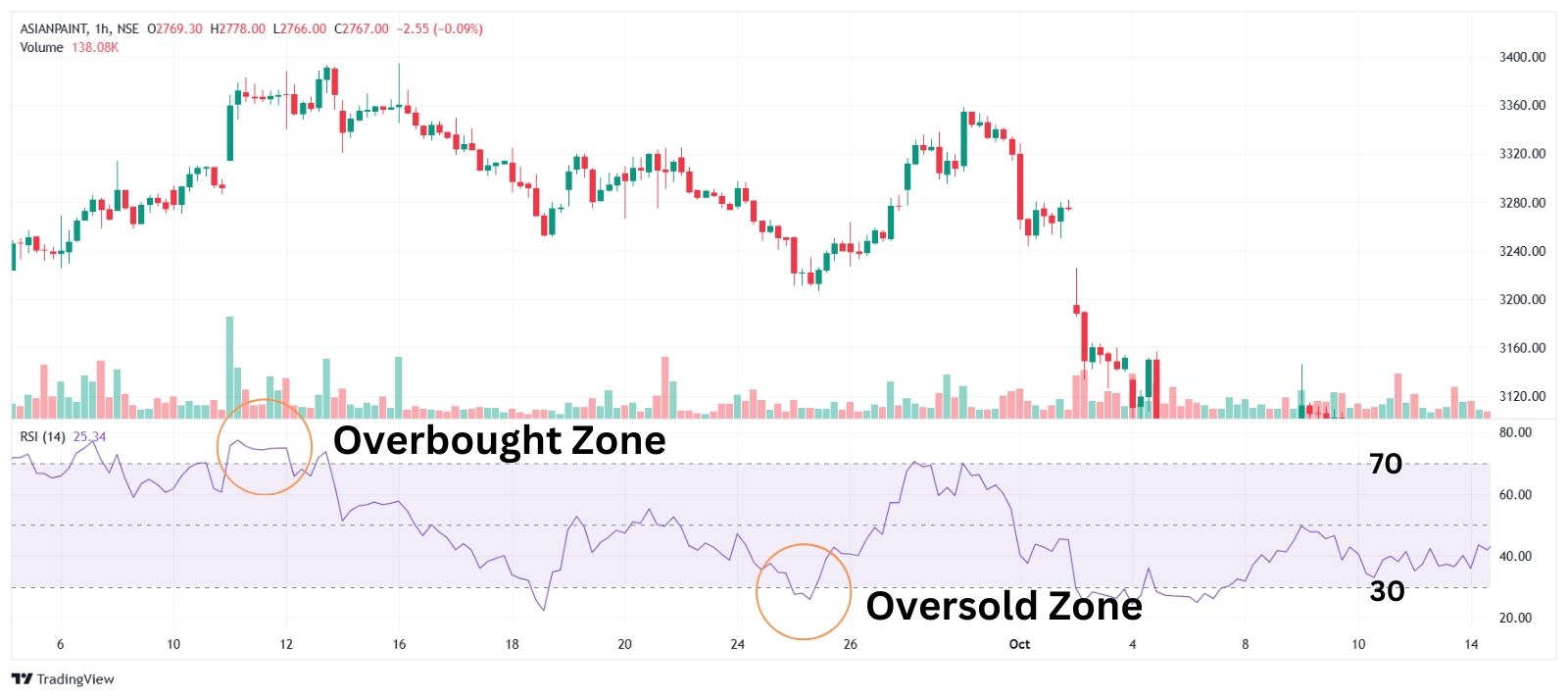
This is 1 Hour Chart of ASIANPAINTS, where the share price decreased when the RSI was above 70 (Overbought Level) and similarly the price got increased when the RSI was under 30 (Oversold Level).
3. Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
MACD is another highly effective indicator that tracks the relationship between two moving averages (typically the 12-day and 26-day EMAs). This tool is widely used by swing traders for its ability to indicate both the direction and momentum of a trend.
How to Use MACD in Swing Trading
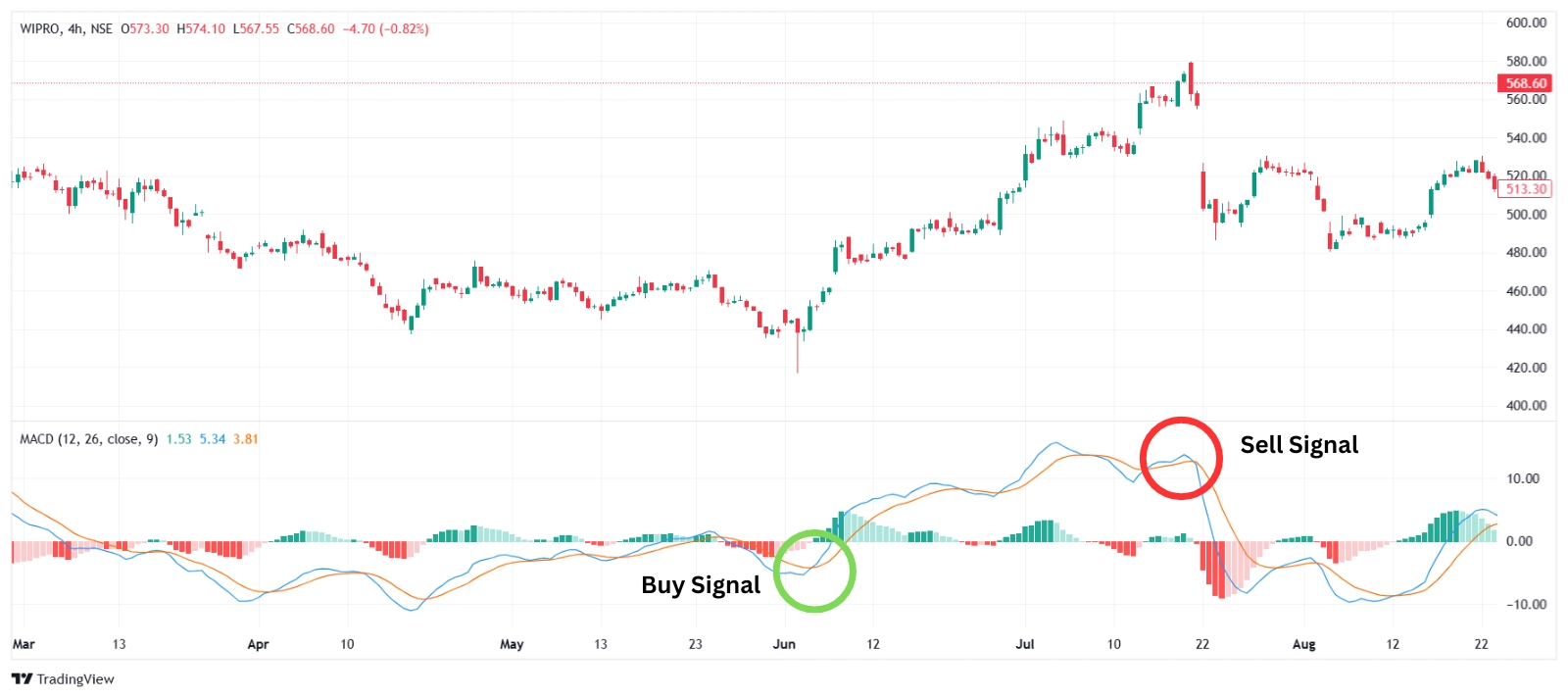
- MACD Line and Signal Line: The MACD line crossing above the signal line suggests a potential buying opportunity, while crossing below indicates a possible selling signal.
- MACD Histogram: The histogram shows the difference between the MACD and signal lines, with larger bars indicating stronger momentum.
4. Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: a Simple Moving Average (usually 20-day) in the middle and two bands plotted above and below it at two standard deviations. These bands expand and contract based on market volatility.
How to Use Bollinger Bands for Swing Trading
- Squeeze: When the bands contract tightly, it signals low volatility and a potential breakout.
- Reversal at the Bands: When the price hits the upper band, it may be overbought, signaling a reversal to the downside. Likewise, if it touches the lower band, it may be oversold.
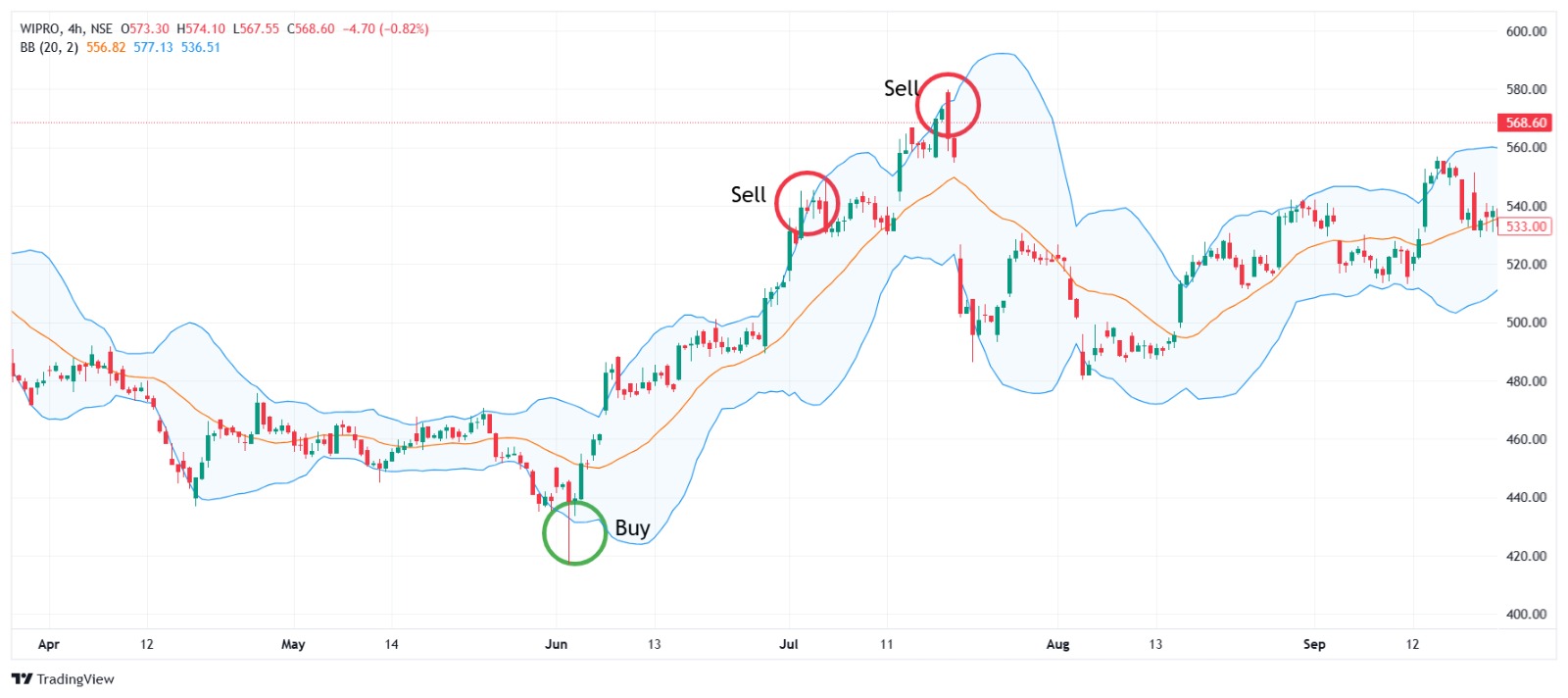
5. Volume Indicators
Volume is a crucial factor in any trading strategy because it reflects the strength behind a price move. Two popular volume indicators are On-Balance Volume (OBV) and Volume Moving Average.
How to Use Volume Indicators in Swing Trading
- On-Balance Volume (OBV): Measures cumulative volume by adding up-days and subtracting down-days. If the OBV is rising, it suggests buying pressure, while a falling OBV indicates selling pressure.
- Volume Moving Average: Analyzing volume against its moving average can confirm if a breakout or trend is supported by strong activity.
6. Stochastic Oscillator
The Stochastic Oscillator compares a stock’s closing price to its price range over a specific period. It ranges from 0 to 100, where values above 80 signal overbought conditions, and values below 20 indicate oversold conditions.
How to Use Stochastic Oscillator in Swing Trading
- Overbought and Oversold Levels: Like RSI, a reading above 80 suggests an overbought condition, while a reading below 20 indicates oversold.
- Crossovers: The oscillator has two lines, %K and %D. A crossover of %K above %D suggests a buying opportunity, while %K crossing below %D signals a sell.
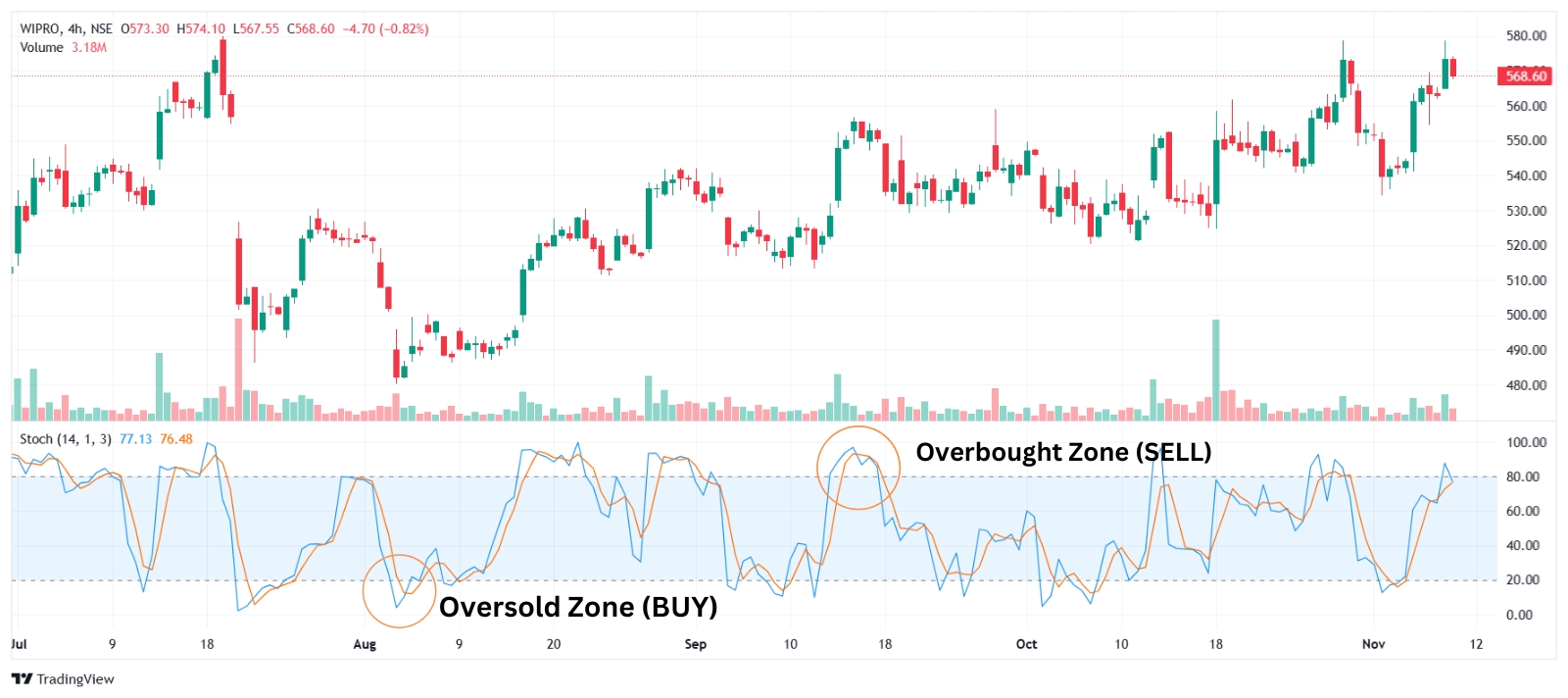
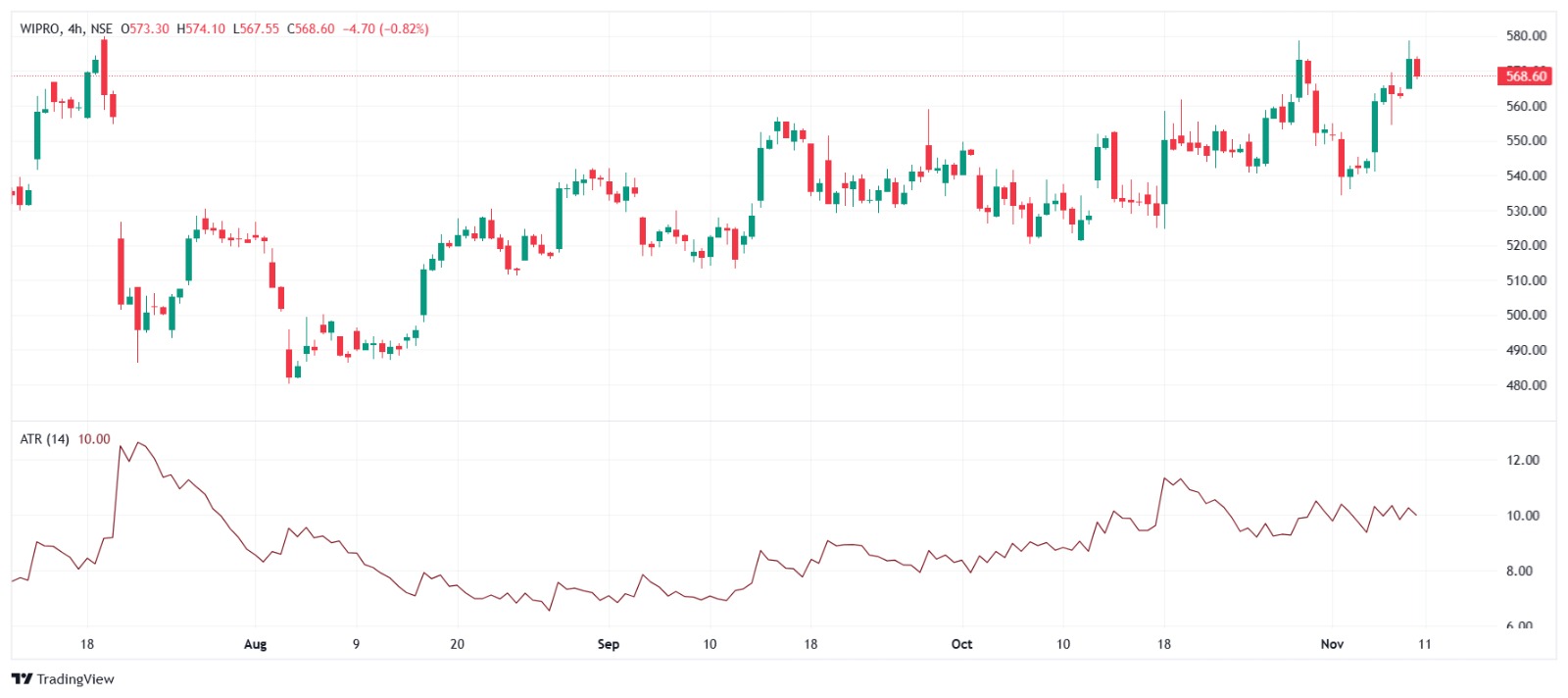
7. Average True Range (ATR)
ATR is a volatility indicator that shows the average range within which a stock moves during a given period. It’s useful for setting stop-loss levels and understanding price movement.
How to Use ATR in Swing Trading
- Volatility Measurement: A high ATR suggests a volatile market, while a low ATR signals stability.
- Stop-Loss Placement: ATR can help determine appropriate stop-loss levels. For example, a stop-loss at 1.5x the ATR value gives the trade room to move without prematurely closing.
8. Parabolic SAR
The Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse) is an indicator that places dots above or below price candles to show potential trend reversals. When the dots are below the price, it signals an uptrend, and when they’re above, it suggests a downtrend.
How to Use Parabolic SAR
- Trend Identification: Dots below the price signal an upward trend, while dots above indicate a downward trend.
- Entry and Exit Signals: When the dots flip from below to above or vice versa, it’s a potential signal to enter or exit a trade.
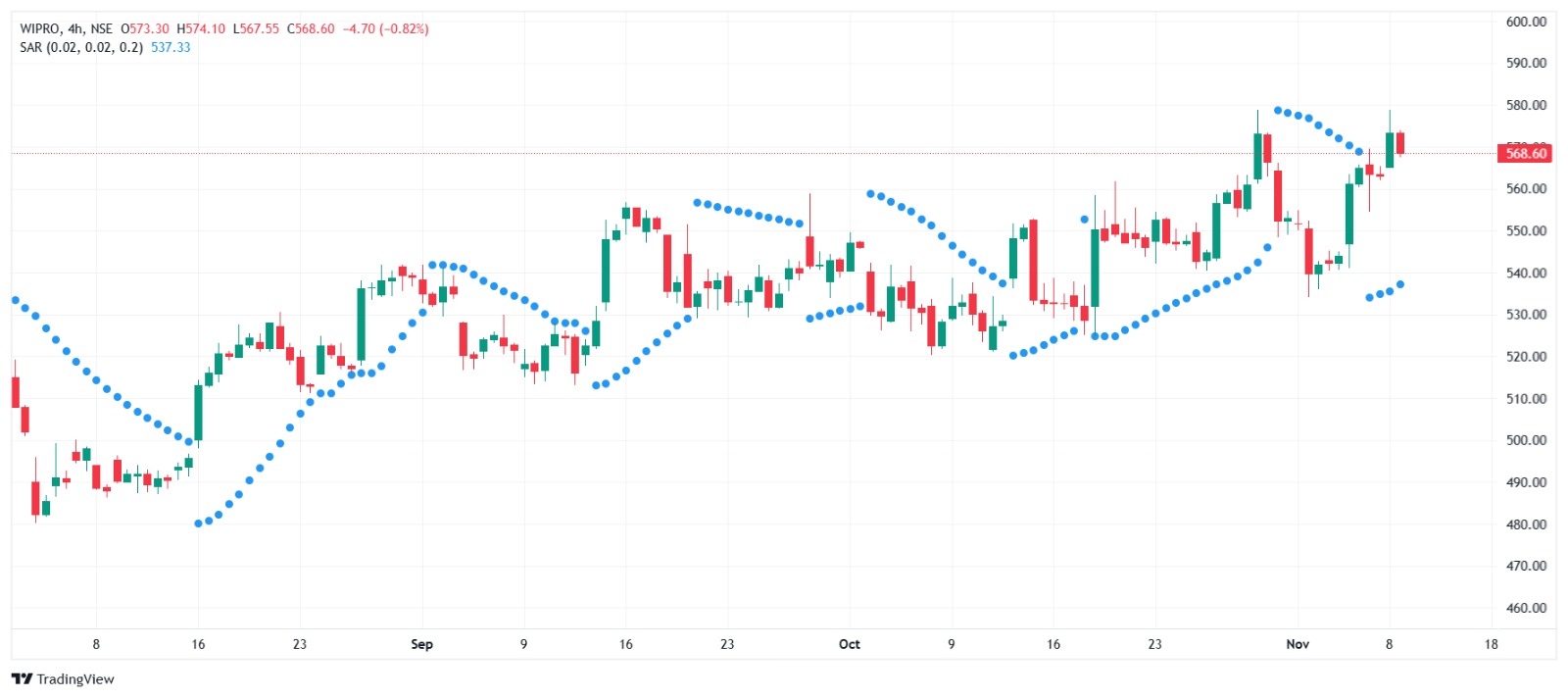
9. Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci Retracement is based on a sequence of numbers that often appear in natural patterns and can help predict potential support and resistance levels in swing trading.
How to Use Fibonacci Retracement
- Identifying Key Levels: Draw the retracement levels (usually at 23.6%, 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%) from a recent peak to a trough, and look for price reactions at these levels.
- Support and Resistance: Price often pauses or reverses at these levels, which can help you set stop-loss and target levels.
10. Ichimoku Cloud
The Ichimoku Cloud is a complex indicator but useful for beginner swing traders once they understand its components. It consists of five lines, including the cloud itself, which shows support and resistance zones, trend direction, and momentum.
How to Use Ichimoku Cloud
- Trend Confirmation: When the price is above the cloud, it signals an uptrend; below the cloud suggests a downtrend.
- Support and Resistance: The cloud itself acts as a potential support or resistance zone.
Also Read: Swing Trading For Beginners: Complete Guide
Combining Indicators for Stronger Swing Trading Signals
For stronger signals in swing trading, consider combining two or more indicators to confirm your trade. For example:
- RSI and Bollinger Bands: If the RSI shows oversold conditions and the price is near the lower Bollinger Band, it could indicate a good buying opportunity.
- MACD and Moving Averages: Use MACD crossovers in combination with a 50-day moving average trend to confirm momentum in the trend direction.
Final Thoughts on Technical Indicators for Swing Trading
Learning these essential technical indicators for swing trading can set you on the path to making informed, confident trades. While indicators provide valuable insights, they’re not foolproof. It’s wise to practice your strategies through a demo account or paper trading before going live.
As you gain experience, you’ll find the best combination of indicators and strategies that work for you. Happy trading!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which is the best indicator for swing trading?
Answer: There isn’t a single “best” indicator for swing trading, as each indicator provides unique insights. However, some of the most popular indicators for swing trading are Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). Moving Averages help with identifying the overall trend, while RSI shows overbought or oversold conditions, and MACD indicates momentum and trend changes. Many traders find that combining these indicators leads to better signals and fewer false entries.
2. How do you predict swing trades?
Answer: Swing trades are predicted by analyzing market trends, price movements, and key technical indicators. A common approach is to look for indicators that signal trend reversals, such as:
- RSI: Values above 70 indicate overbought conditions, while below 30 indicates oversold, hinting at possible trend reversals.
- MACD Crossovers: When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it often signals a buy; when it crosses below, it’s a potential sell signal.
- Support and Resistance Levels: By plotting levels where the price has repeatedly reversed, traders can predict potential price swings as the price approaches these levels.
- Volume: High trading volume along with a price breakout often confirms the strength of a trend.
Using these indicators together gives a more reliable prediction than any single indicator.
3. What is the best RSI setting for swing trading?
Answer: The default RSI setting of 14 periods is widely used in swing trading and is effective for most scenarios. However, some swing traders adjust the RSI period based on their specific trading style:
- 9 or 10-period RSI: A shorter period setting, making the RSI more sensitive and providing quicker signals, which can be useful for fast-paced markets or shorter swings.
- 21-period RSI: A longer period, providing smoother signals and better suited for traders focusing on fewer but more reliable signals over longer swings.
Ultimately, it’s best to experiment with different RSI settings and back-test them to find what works best for your style.
4. Is MACD good for swing trading?
Answer: Yes, the MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) is an excellent indicator for swing trading. It’s particularly useful because it helps identify both the direction and momentum of a trend. Here’s how swing traders often use MACD:
- MACD Crossovers: When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it’s considered a bullish signal, suggesting it may be time to enter a long (buy) position. Conversely, when it crosses below, it indicates a bearish signal, which might be a time to sell or short.
- Histogram Bars: The MACD histogram bars show the difference between the MACD line and the signal line, with larger bars indicating stronger momentum. When bars start shrinking, it suggests momentum may be weakening, often signaling an upcoming trend reversal.
Due to its versatility, many swing traders rely on MACD in combination with other indicators, like RSI or Moving Averages, to confirm their trades and avoid false signals.